In a competitive market, packaging often serves as consumers’ first impression of a product, making the selection of printing techniques a crucial element of brand representation. As technology progresses and creativity thrives, custom packaging design continues to evolve, presenting endless possibilities.
To make your packaging unique and eye-catching, various printing methods are available. Some of the most common methods include lithography, flexography, and rotogravure, among others.
Each printing technique offers distinctive characteristics, allowing brands to Kraft packaging that aligns with their style and color palette, ultimately enhancing brand identity and consumer appeal. Understanding the merits and demerits of each method is essential to making the best choice.
In this article, we will explore these printing methods one by one, along with their pros and cons, to help you make an informed decision.
So, let’s get started.
Printing Techniques in the Packaging Industry

Printing is not a new concept; however, printing techniques have changed significantly during different eras. There is a vast variety of ways they can be done depending on what one wants.
They go from old methods like letterpress and lithography to new ones, such as digital printing, where each one has special features which have led to changes in how we make printed stuff.
Such skills differ not only in how they work but also in the type of things they are made of and the kind of results you get including speed for example.
Let’s explore some of the most commonly used printing techniques for custom packaging;
Lithography
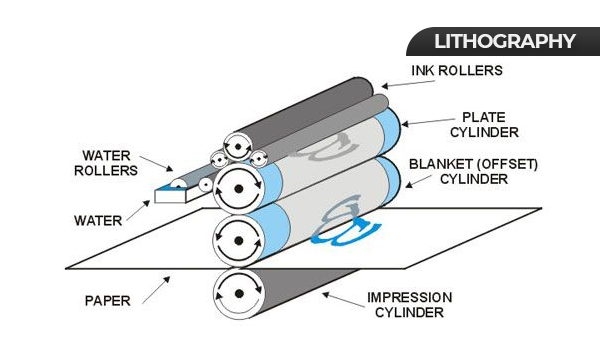
Lithography, also known as offset printing, stands as a favored printing technique across various marketing materials, spanning from business cards to promotional sheets.
Additionally, it finds extensive application in packaging, notably in the production of folding cartons and litho labels, commonly utilized for labeling.
Lithography finds widespread application for flat items such as custom folding cartons, and expansive labels used in packaging and displays. Lithography printing for packaging provides business owners with an opportunity to make packaging using a high-end retail quality look.
Pros:
- Unmatched color accuracy
- High-quality printing
- Variety of coatings, like matte and glossy
- Well-suited for high-volume production
Cons:
- Limited effectiveness on non-flat surfaces.
- Relatively higher costs
- Longer lead times for production
Flexography
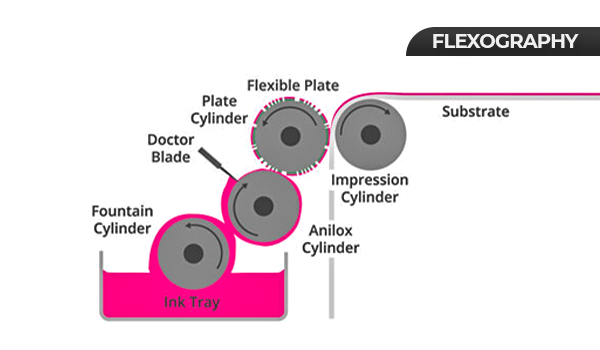
Flexographic printing, also known as “flexo,” can be used on metals, papers, and plastics, making it more useful in the printing industry and more feasible to use. In flexography printing, a specialized roller feeds each flexible plate with ink, with a single flexible plate required for each individual printed color.
Flexo has also stood as the preferred method for high-volume product labels and flexible packaging production in the food and beverage industry. Printing for flexible packaging is growing increasingly common due to the various advantages this packaging kind offers.
Besides that, it’s cost-effective if a large number of orders are placed at the same time. Flexography printing is used to make items such as gift wrap, tissue paper, napkins, shopping bags, envelopes, and more.
Pros:
- Utilize both water- and oil-based inks
- Allowing the printing of almost any shape or format
- Ideal for high-volume runs
- Cost-effective per unit
Cons:
- Lower printing quality than lithography
- Limited coating options
- Difficult replicating photo-quality images
Rotogravure
Rotogravure is used to print larger surfaces, which require a lot of ink to enhance their quality. The image in rotogravure is engraved onto a cylinder because, like offset printing and flexography; it uses a rotary printing press.
Primarily recommended for detailed packaging designs, which excel in reproducing intricate details and vibrant colors, Gravure is the usual choice for food products packaged in flexible materials.
Rotogravure printing is usually used for very large batches of production of packaging. Gravure provides excellent results for long runs.
Pros:
- Premium quality images
- High volume production
Cons:
- Lack of coating options
- High investment in tooling
- Expensive for low-volume printing
Digital Printing
Digital printing has rapidly become a mainstream choice due to its faster speeds and gaining fame in product packaging as among the most flexible printing techniques.
It can be used with a minimal amount of equipment and materials. It can also produce the products in smaller quantities with minimum effort. Digital printing imposes the image straight into the media substrate rather than transferring it via metal plates.
Digital printing is a qualitative method for printing labels, boxes, folding cartons, prototypes, shirts, custom tumblers, and much more.
Pros:
- Minimum tools needed
- Enhanced print quality
- Very little tooling or setup costs
- Suitable for small formats and quantities
- Quick printing
- Best choice for small-scale companies/industries
Cons:
- Smooth color is challenging
- Expensive for high-volume printing
Silkscreen Printing
Screen printing offers undefeatable ink thickness, and silkscreen printing generates a clear, sharp finish with printed text and images, making it perfect for creating tactile and visually striking packaging.
Silkscreen printing works when the ink passes through the open spaces and is absorbed into the fabric beneath, creating a design for the product.
Silkscreen printing uses clothing mesh. The ink is spread on the cloth, and the image is printed on boxes. Silkscreen printing is also used on non-flat surfaces.
Pros:
- Generates a clear, sharp finish
- Excellent for promotional items
- Best at lower-volume production
- Cost-effective solution with relatively low setup costs
Cons:
- Slower production
- Not suitable for high-volume printing
- Challenges to get high-quality pictures
Thermography Printing
Thermographic printing, or raised printing, relies on heat to create letters or images on paper. It uses offset printing with resin to give the packaging design surface a shiny look.
Thermography is regarded as an appealing and preferred printing process that adds prestige to the product.
Pros
- Raise printing value
- Gives a professional look
- Cost-effective
Cons:
- Not eco-friendly due to heat production
- Expensive equipment
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate printing technique for custom packaging ensures it aligns seamlessly with your brand’s aesthetics and objectives.It’s important to note that each method discussed above lithography, flexography, rotogravure, digital printing, and silkscreen printing has its own advantages and limitations.
With lithography’s unmatched color accuracy, Flexography’s affordable high-volume production runs, rotogravure’s premium-quality images for long production batches, and digital printing’s flexibility for small-scale ventures, there’s a solution tailored to every packaging need. Additionally, with its clear, sharp finish, silkscreen printing is particularly suited to visually striking packaging and promotional items.
By understanding the distinct features of each printing technique, businesses can make informed decisions and create appealing packaging that effectively communicates their brand identity and message to consumers.



